If you’re new to web development or have been curious about server-side programming, chances are you’ve heard of Node.js. But what exactly is Node.js, and why is it so popular among developers today? This article will give you a simple introduction to Node.js for a beginner-friendly introduction to Node.js, why it’s useful, and how you can get started.
What is Node.js
Node.js is a runtime environment that allows you to run JavaScript outside a web browser. It is commonly used for backend development to build fast and scalable server-side applications.
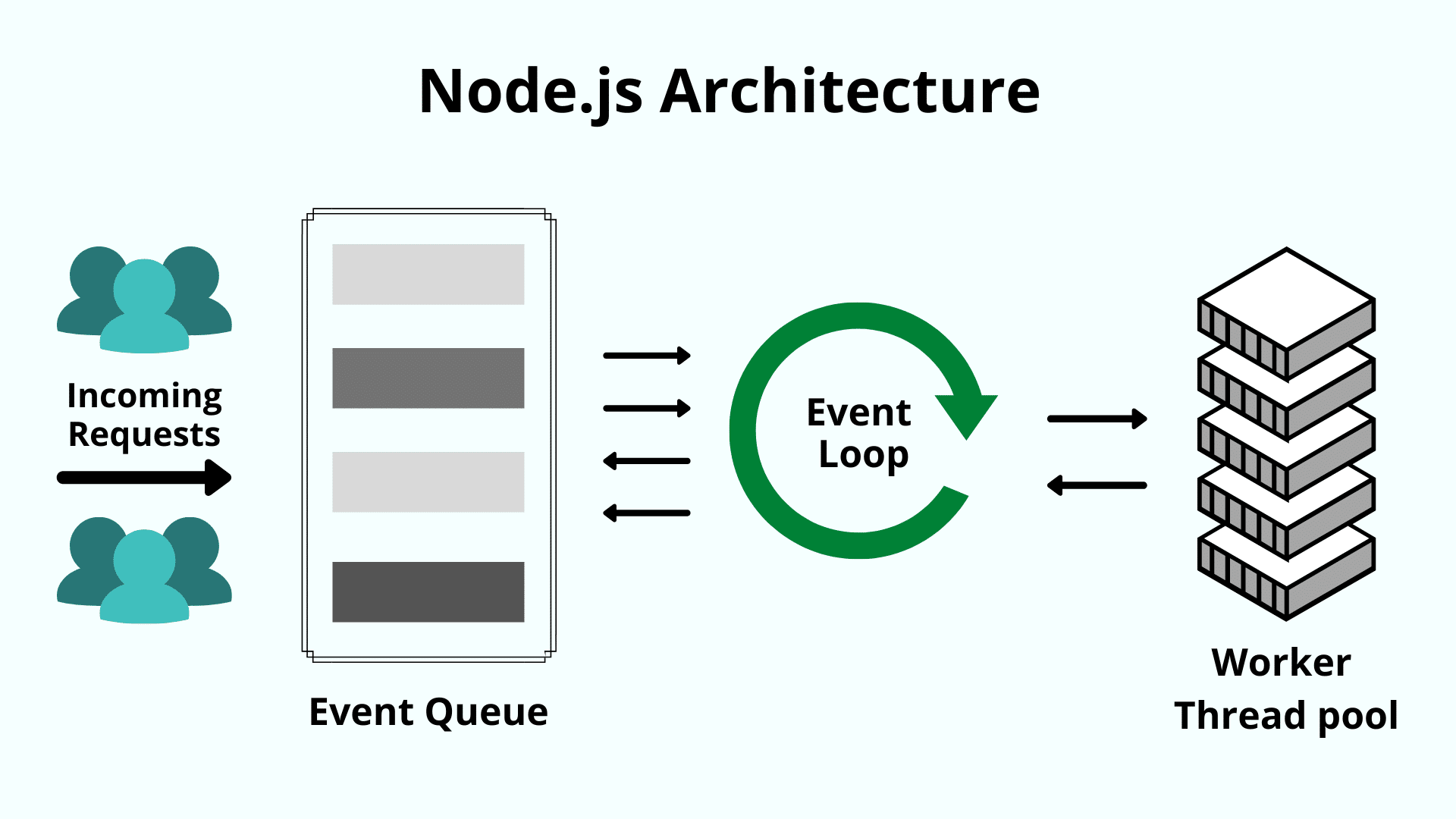
Why Use Node.js?
Uses JavaScript for both frontend & backend
Fast and scalable due to its non-blocking architecture
Has a huge library of open-source packages (npm)
Used by big companies like Netflix, PayPal, and LinkedIn
Installing Node.js
Step 1: Download & Install
- Go to Node.js.org
- Download the LTS (Long-Term Support) version
- Install it (Make sure npm is included)
Step 2: Check Installation
Open Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Mac/Linux) and type:
node -v
This should show the installed version of Node.js.
To check npm (Node Package Manager):
npm -v
Creating Your First Node.js App
1. Create a Project Folder
Open the terminal and run:
mkdir my-node-app cd my-node-app
2. Initialize a Node.js Project
npm init -y
This creates a package.json file, which manages dependencies and configurations.
3. Creating a Simple Node.js Server
Create a file called server.js and open it in a code editor (e.g., VS Code).
Write this code in server.js
const http = require("http");
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "text/plain" });
res.end("Hello, Node.js Server!");
});
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("Server is running on port 3000");
});
4. Run the Server
terminal, run:
node server.js
5. Test Your Server
http://localhost:3000
You should see “Hello, Node.js Server!”
Using Express.js (A Node.js Framework)
Express.js is a popular framework for building web applications in Node.js.
1. Install Express
npm install express
2. Create an Express Server (server.js)
const express = require("express");const app = express();
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.send("Hello from Express.js!");
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("Server running on port 3000");
});
3. Start the Express Server
node server.js
http://localhost:3000
“Hello from Express.js!”
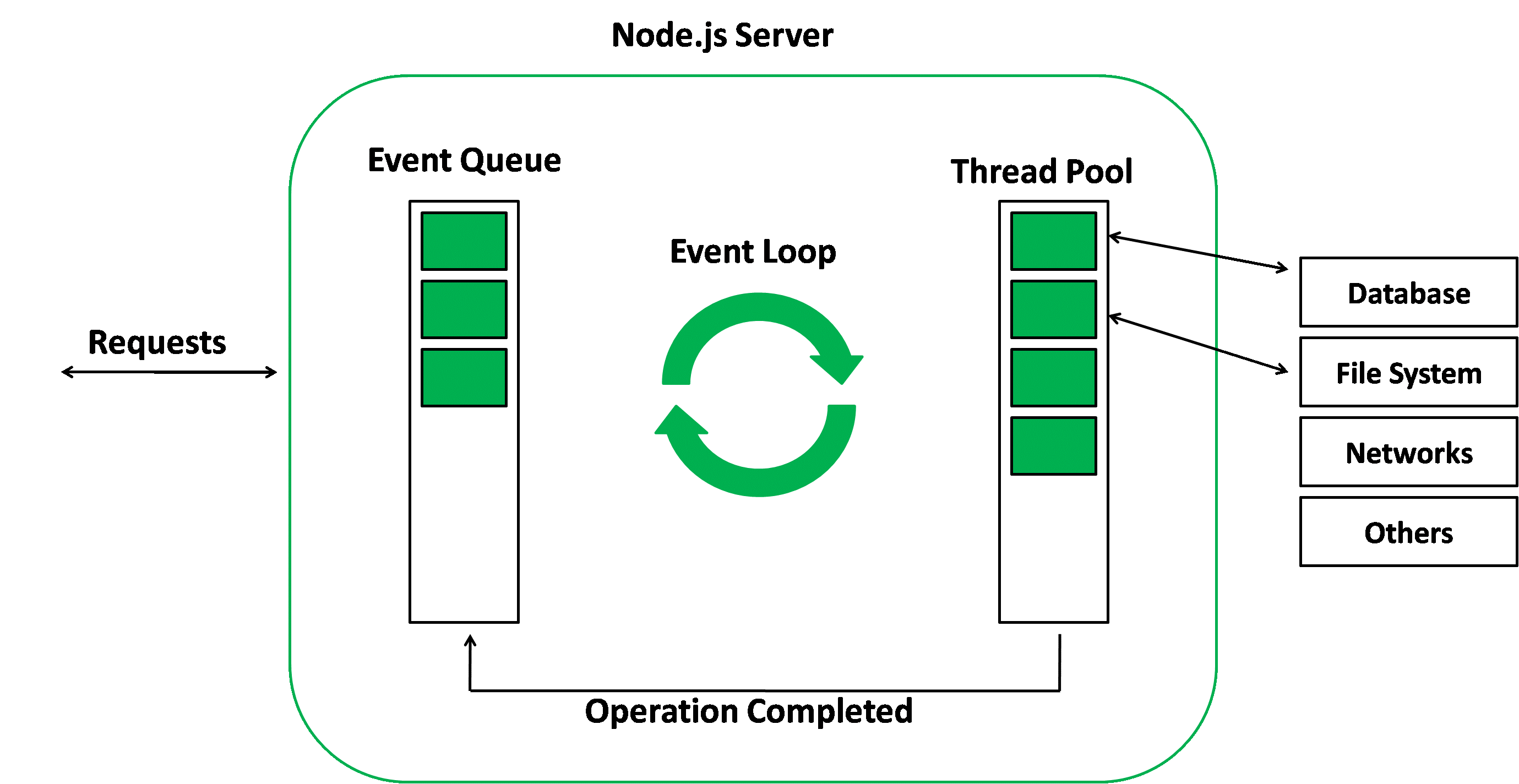
1. Requests:
The request is coming from the client side, and the user wants a response from the server to act on. These actions may be non-blocking, simple, or they may be blocking, complex tasks.
2. NodeJS Server:
Node.js is used on the server side. It receives incoming client requests from users, processes them, and responds to the specific client or user.
3. Event Queue:
In Node.js event queue stores the requests and passes them one by one into the event loop.
4. Event Loop:
The event loop receives the request from the event queue, processes the request, and returns the response to the particular client.
5. Thread Pool:
The thread pool consists of the available threads in our Node.js server, which will take some tasks to complete the client request.
6. External Resources:
External resources are those that need to fulfill the blocking operations in client requests. These resources can be used for computation, data storage, and other purposes.
Read Also:
Getting Started with the MERN Stack: A Beginner’s Guide
Introduction to Node.js for Beginners
Also Visit:
http://www.inimisttech.com